Author: Gihyun Kim
Date: May 23rd, 2024
Topic: The Greedy Algorithm
What is the Greedy Algorithm?
The greedy algorithm works by selecting the best possible option shown at the given moment regardless of whether it will bring the best possible outcome. This algorithm never returns and fixes the decision that it has made even if the result is not the best possible outcome available. It tends to select the best option at a local scale in order to find the best option and outcome at a global scale.
Benefits:
The very definition of the greedy algorithm allows it to have some crucial benefits such as efficiency (in some cases) and simplicity. The greedy approach is very similar to human intuition in that it selects the local best option to find the global best outcome. This makes the code simple to demonstrate and easy to understand. It can also bring efficiency in cases suited to the greedy approach. These situations are called greedy property where making locally optimal choices at each step leads to a globally optimal solution. In cases like this, the greedy algorithm can prove to be much more efficient compared to DFS and BFS or other searching algorithms that require a full go-through of the data structure.
Disadvantages:
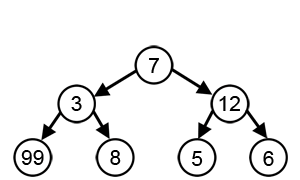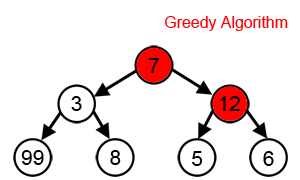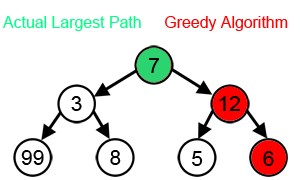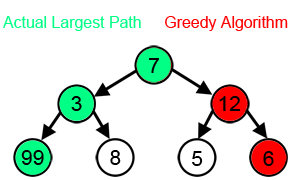
Despite its perks, the greedy algorithm has some crucial downsides to it that make the use of it quite restricted. As shown in the image above (at the top of the page), at times where the local best option does not lead to the global best solution, the algorithm tends to deviate from the actual best option. Also, as this algorithm does not use backtracking to return to a certain node, it cannot fix past decisions and in cases where the greedy property is not met, it can be quite inefficient.
Example of use:
Problem:
You are trying to weigh an object using a two-arm scale.
At the end of both arms of this scale, there are plates on which objects or weights are placed, and both arms are the same length. in addition, only scale weights can be placed on one side of the scale, and only objects to be weighed can be placed on the other side.
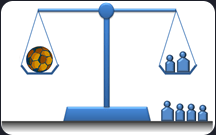
Given N balance weights whose weights are positive integers, write a program that uses these weights to find the minimum weight of an immeasurable positive integer.
For example, given seven balance weights with weights of 3, 1, 6, 2, 7, 30, and 1, respectively, the smallest of the positive integer weights that cannot be measured with these weights is 21.
Input:
7
3 1 6 2 7 30 1
Output:
21
My Problem:
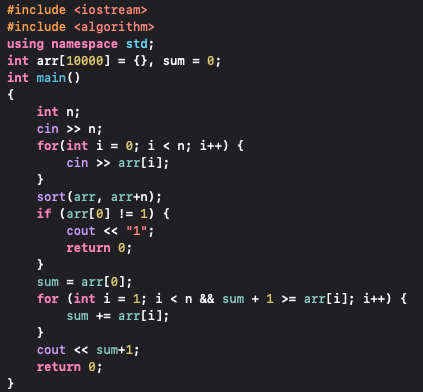
Problem & Image source: https://www.jungol.co.kr/problem/2499?cursor=eyJwcm9ibGVtc2V0IjoiOCIsImZpZWxkIjoyLCJpZHgiOjV9

Leave a comment